Periodic table of elements brainpop – BrainPOP’s Periodic Table of Elements embarks on a captivating journey, illuminating the fundamental principles that govern the very essence of matter. This interactive resource unveils the secrets of the elements, their properties, and their profound impact on our world.
Through engaging animations and expert explanations, BrainPOP’s Periodic Table of Elements fosters a deep understanding of the organizing principles that shape the chemical landscape. It empowers learners to explore the periodic trends, group characteristics, and reactivity patterns that define each element.
Periodic Table Overview
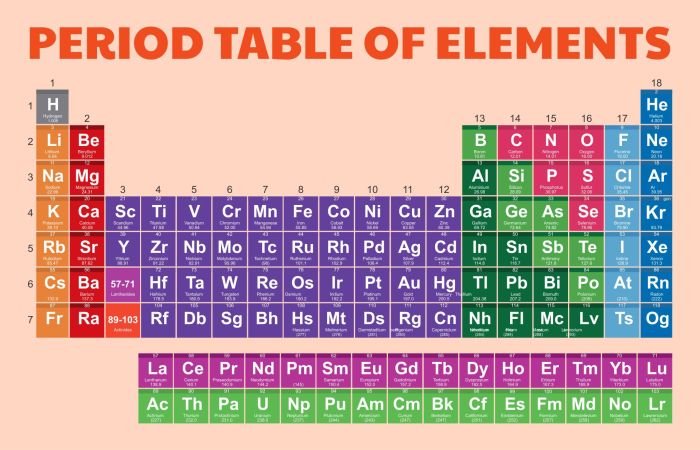
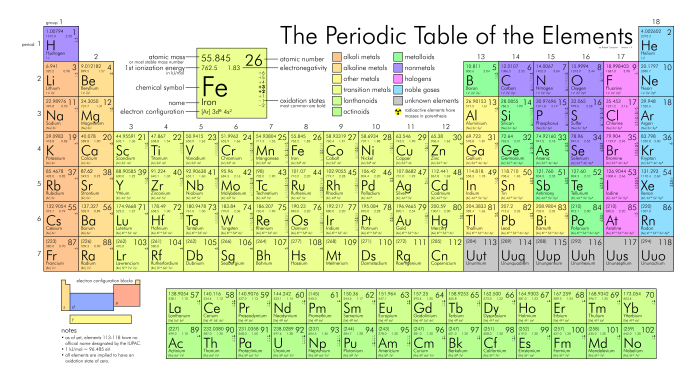
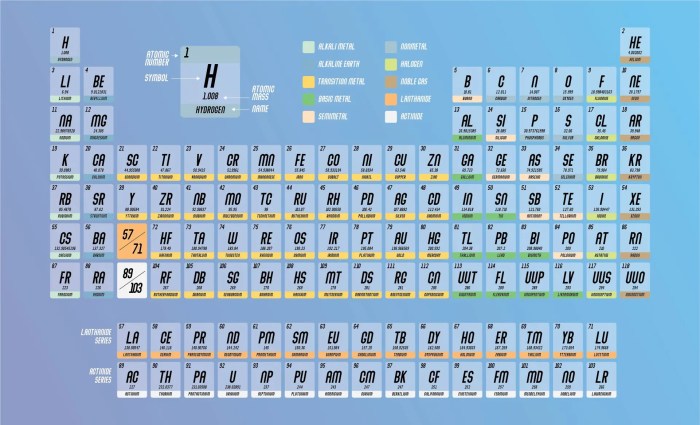
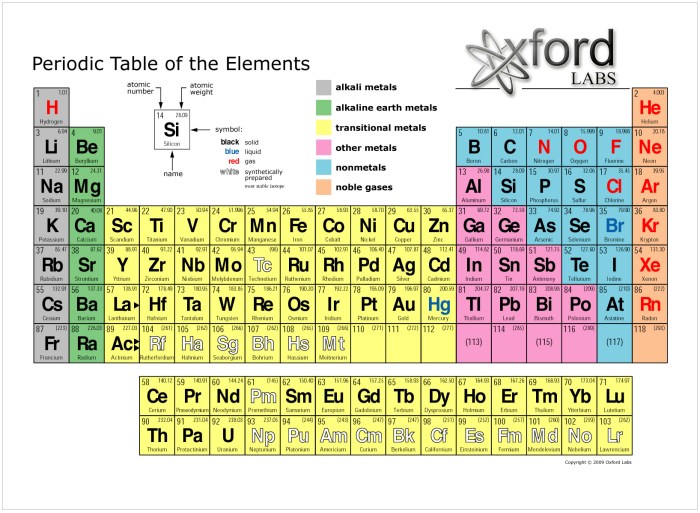
The periodic table of elements is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. It provides a systematic and comprehensive representation of all known elements, serving as a valuable tool for understanding the behavior and interactions of matter.
The periodic table was developed over time, with significant contributions from scientists like Dmitri Mendeleev and Henry Moseley. Its organization has played a crucial role in advancing our understanding of chemistry and the properties of elements.
Elements are arranged in the periodic table according to their atomic number, which is the number of protons in their nuclei. The rows of the table, known as periods, represent increasing atomic numbers. The columns of the table, known as groups, represent elements with similar chemical properties due to their shared electron configurations.
Element Properties and Trends, Periodic table of elements brainpop
The periodic table allows us to identify and understand key properties of elements, including atomic mass, electronegativity, and ionization energy.
- Atomic mass:The average mass of an element’s atoms, taking into account the isotopes and their relative abundances.
- Electronegativity:The ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself, influencing chemical bonding and reactivity.
- Ionization energy:The energy required to remove an electron from an atom, providing insights into the stability of atoms and their tendency to form ions.
These properties exhibit periodic trends across the table. For instance, electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a period and decreases from top to bottom within a group.
Groups and Periods
The periodic table is divided into vertical columns called groups and horizontal rows called periods.
Groups:Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties due to their identical valence electron configurations. For example, all elements in Group 1 (alkali metals) have one valence electron, making them highly reactive.
Periods:Elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells. As we move from left to right across a period, the atomic number and the number of electrons in the outermost shell increase, leading to changes in chemical properties.
Reactivity and Bonding
The position of an element in the periodic table provides insights into its reactivity and bonding behavior.
Reactivity:Elements in the same group generally have similar reactivity due to their shared valence electron configurations. For instance, alkali metals (Group 1) are highly reactive due to their single valence electron, while noble gases (Group 18) are relatively unreactive because their valence shells are filled.
Bonding:The electron configuration of an element determines its ability to form chemical bonds. Elements with unpaired electrons in their valence shells tend to be more reactive and can form bonds to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Quick FAQs: Periodic Table Of Elements Brainpop
What is the significance of the periodic table?
The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and chemical properties, providing a systematic framework for understanding the behavior and interactions of matter.
How does the periodic table help us predict element properties?
The periodic trends observed in the table allow scientists to predict the properties of elements based on their position, enabling them to make informed inferences about their reactivity, bonding behavior, and physical characteristics.
What are the practical applications of the periodic table?
The periodic table finds widespread use in various fields, including chemistry, materials science, and medicine, guiding the development of new materials, drugs, and technologies that shape our modern world.