Rank the following elements in order of increasing electronegativity. – Rank the following elements in order of increasing electronegativity: Hydrogen (H), Carbon (C), Nitrogen (N), Oxygen (O), Fluorine (F). Electronegativity, a crucial concept in chemistry, measures an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. Understanding electronegativity enables chemists to predict bond polarity, molecular shape, and compound reactivity, providing insights into the behavior of matter.
The periodic trends of electronegativity, influenced by factors such as atomic radius, nuclear charge, and electron shielding, reveal fascinating patterns. As we move across a period from left to right, electronegativity generally increases, while moving down a group, it decreases.
This knowledge empowers us to comprehend the chemical bonding and properties of various elements and compounds.
Electronegativity Definition and Background
Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. It is an intrinsic property of an element that determines its reactivity and bonding behavior. Elements with high electronegativity have a strong tendency to attract electrons, while elements with low electronegativity have a weak tendency to attract electrons.
Examples of electronegative elements include fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogen. These elements have high electronegativity values and tend to form ionic or polar covalent bonds. Examples of electropositive elements include sodium, potassium, and calcium. These elements have low electronegativity values and tend to form metallic or nonpolar covalent bonds.
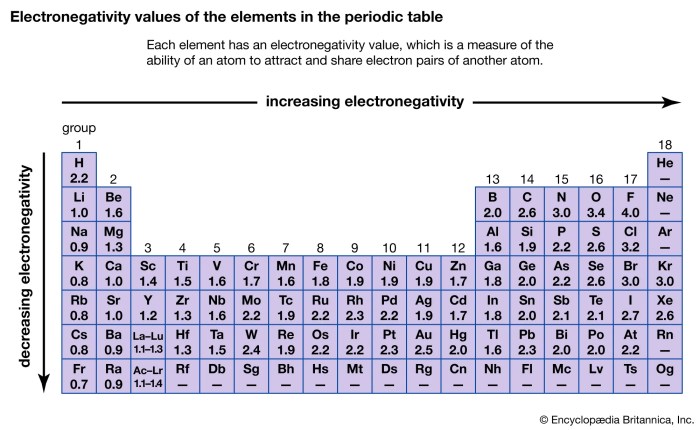
Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a period and decreases from top to bottom within a group in the periodic table.
Ranking Elements by Electronegativity
| Element | Electronegativity |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | 2.20 |
| Carbon (C) | 2.55 |
| Nitrogen (N) | 3.04 |
| Oxygen (O) | 3.44 |
| Fluorine (F) | 4.00 |
The elements are ranked in order of increasing electronegativity, with fluorine being the most electronegative and hydrogen being the least electronegative.
Factors Influencing Electronegativity
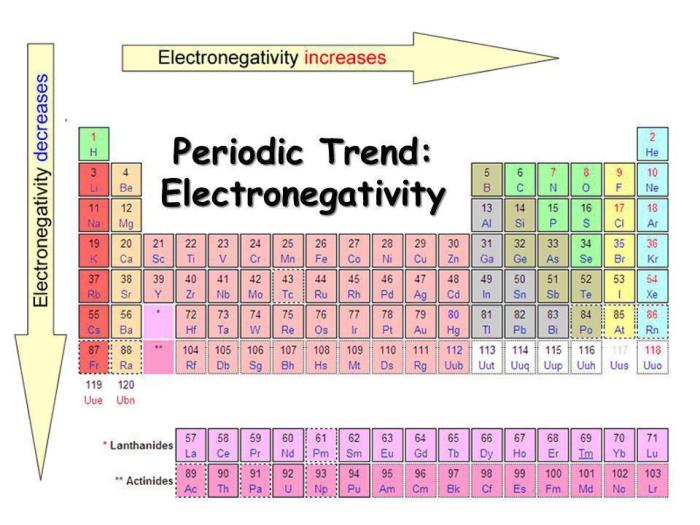
The electronegativity of an element is influenced by several factors, including:
- Atomic radius:Electronegativity generally decreases with increasing atomic radius. This is because the electrons in larger atoms are farther from the nucleus and are less strongly attracted to it.
- Nuclear charge:Electronegativity generally increases with increasing nuclear charge. This is because the nucleus has a stronger attraction for the electrons when there are more protons.
- Electron shielding:Electronegativity generally decreases with increasing electron shielding. This is because the inner electrons shield the outer electrons from the attraction of the nucleus.
Applications of Electronegativity
Electronegativity is a useful concept that can be used to predict the properties of compounds. For example, electronegativity can be used to predict:
- Bond polarity:The difference in electronegativity between two atoms determines the polarity of the bond between them. A bond between two atoms with a large difference in electronegativity will be polar, while a bond between two atoms with a small difference in electronegativity will be nonpolar.
- Molecular shape:The electronegativity of the atoms in a molecule determines the shape of the molecule. Molecules with polar bonds will have a bent or asymmetric shape, while molecules with nonpolar bonds will have a linear or symmetric shape.
- Reactivity of compounds:The electronegativity of the atoms in a compound determines the reactivity of the compound. Compounds with polar bonds will be more reactive than compounds with nonpolar bonds.
FAQ Guide: Rank The Following Elements In Order Of Increasing Electronegativity.
What is electronegativity?
Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond.
Which element has the highest electronegativity?
Fluorine (F) has the highest electronegativity among the given elements.
How does electronegativity affect bond polarity?
Electronegativity differences between bonded atoms create bond polarity, with the more electronegative atom having a partial negative charge.
