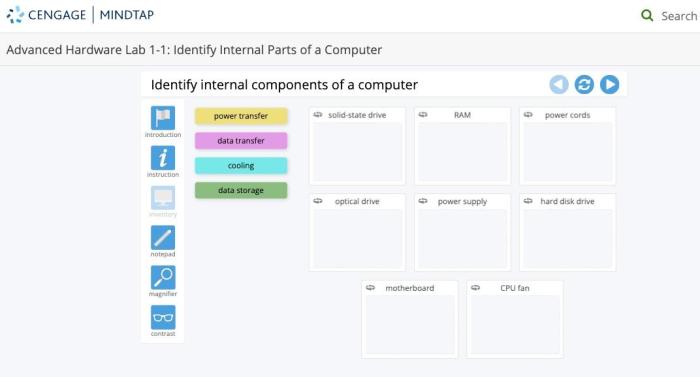
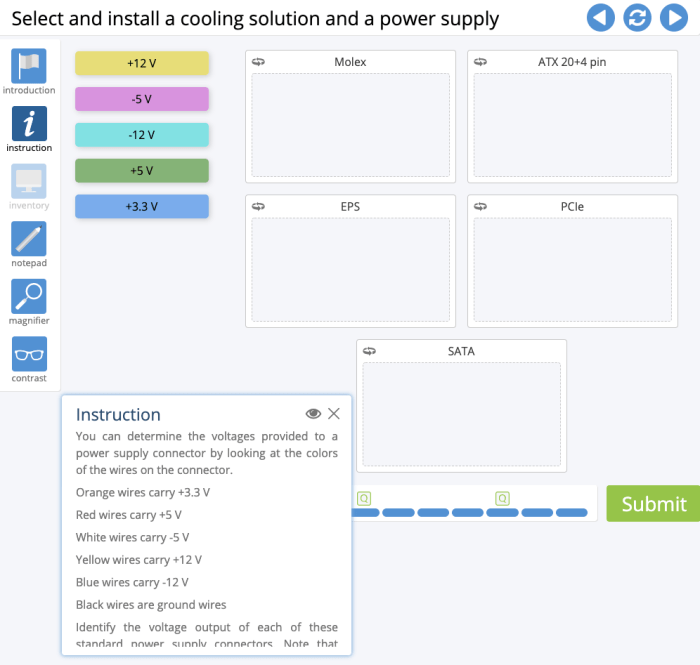
Advanced hardware lab 5-1 select and install a storage drive – Embark on a journey into the realm of advanced hardware labs with this comprehensive guide on selecting and installing a storage drive. Delve into the intricacies of storage drive technology, explore the nuances of different drive types, and master the art of seamless drive installation and configuration.
Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or an aspiring hardware enthusiast, this guide will empower you with the knowledge and skills to navigate the complexities of storage drive selection and installation.
Storage Drive Selection
Selecting the appropriate storage drive for an advanced hardware lab requires careful consideration of several factors, including:
- Performance requirements: The speed at which data can be read and written to the drive.
- Capacity: The amount of data that can be stored on the drive.
- Reliability: The likelihood that the drive will fail and cause data loss.
- Cost: The purchase price and ongoing maintenance costs of the drive.
Different types of storage drives have different advantages and disadvantages. The following table compares the most common types of storage drives used in advanced hardware labs:
| Drive Type | Performance | Capacity | Reliability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDD (Hard Disk Drive) | Lowest | Highest | Lowest | Lowest |
| SSD (Solid State Drive) | Highest | Lower | Higher | Higher |
| NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) | Highest | Lower | Highest | Highest |
General Inquiries: Advanced Hardware Lab 5-1 Select And Install A Storage Drive
What are the key factors to consider when selecting a storage drive for an advanced hardware lab?
Capacity, performance (speed and latency), reliability, cost, and compatibility with the lab’s systems and applications.
What are the advantages of using an SSD (Solid State Drive) over an HDD (Hard Disk Drive)?
SSDs offer significantly faster read/write speeds, lower latency, higher durability, and reduced power consumption compared to HDDs.
How do I configure a RAID array for improved data protection and performance?
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) allows multiple storage drives to be combined into a single logical unit, providing data redundancy, improved performance, and fault tolerance.
What are some common storage drive issues and how can I troubleshoot them?
Common issues include drive failure, data corruption, and performance degradation. Troubleshooting involves identifying symptoms, running diagnostic tests, and implementing appropriate corrective actions.